Advanced Imaging
Building on the knowledge from the Camera Basis articles, this Learn section takes you through the advanced factors to consider when performing cutting-edge imaging or aiming to understand the intricacies involved with imaging with scientific cameras.
These articles will cover aspects such as the differences in performance with certain digital interfaces, camera shutters, triggering, and PRNU/DSNU.
Let’s advance your camera knowledge!
Digital Interfaces
Camera technologies are continually advancing, producing faster cameras with larger sensors. This means that the way that data is transferred from camera to computer is vital, maintaining a sufficient data rate to record activity from your sample.
This article outlines different digital interfaces for Teledyne Photometrics products, from USB to PCIe, and which is right for your imaging.
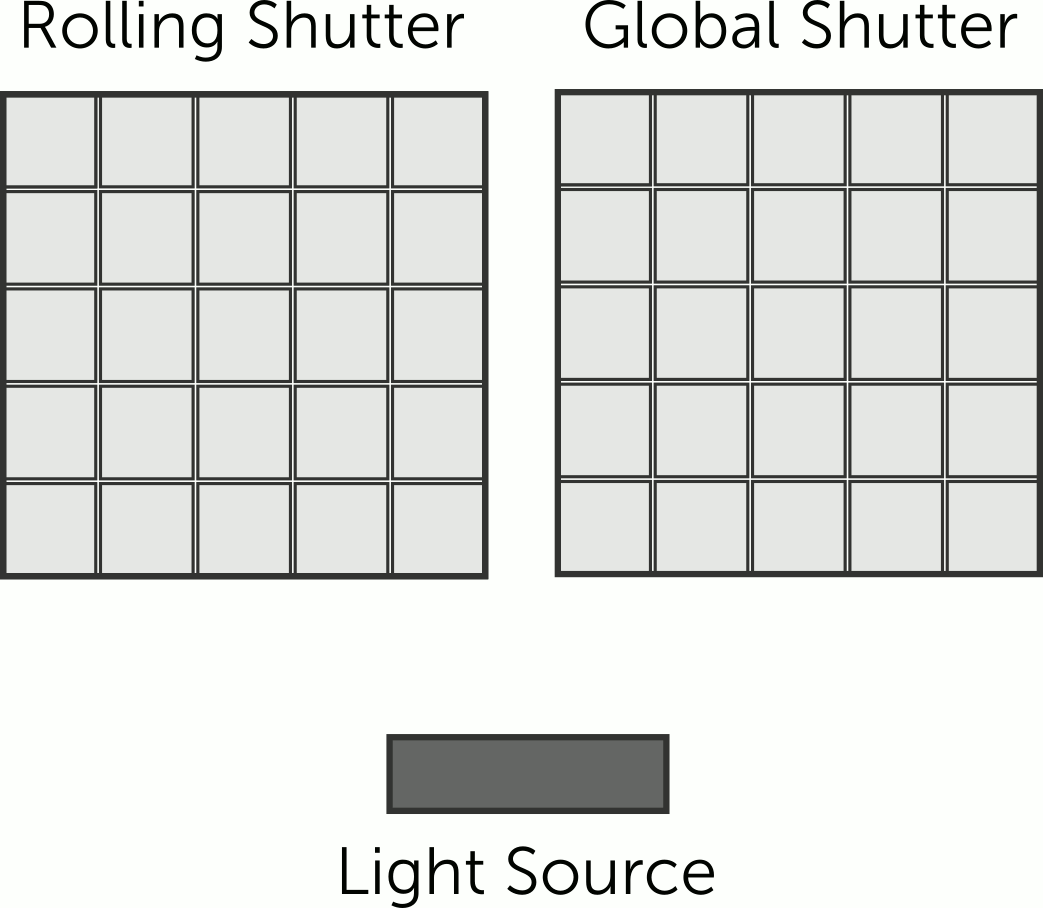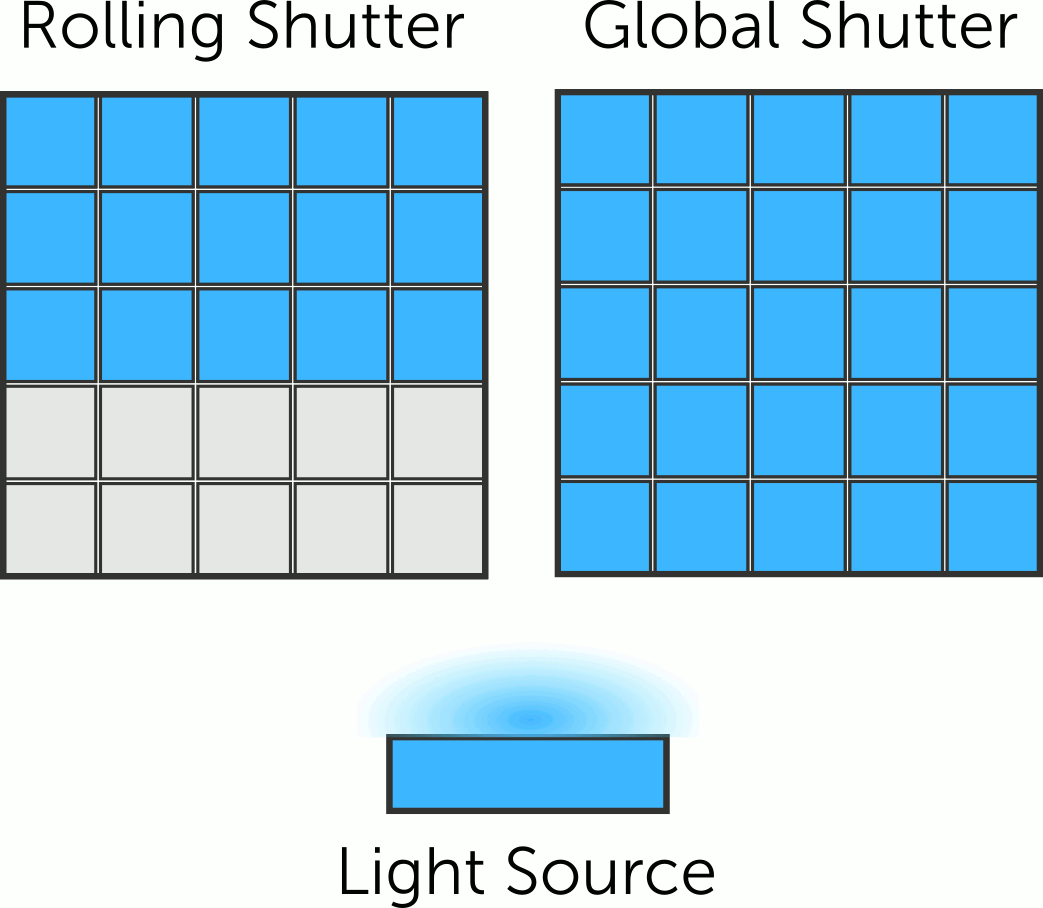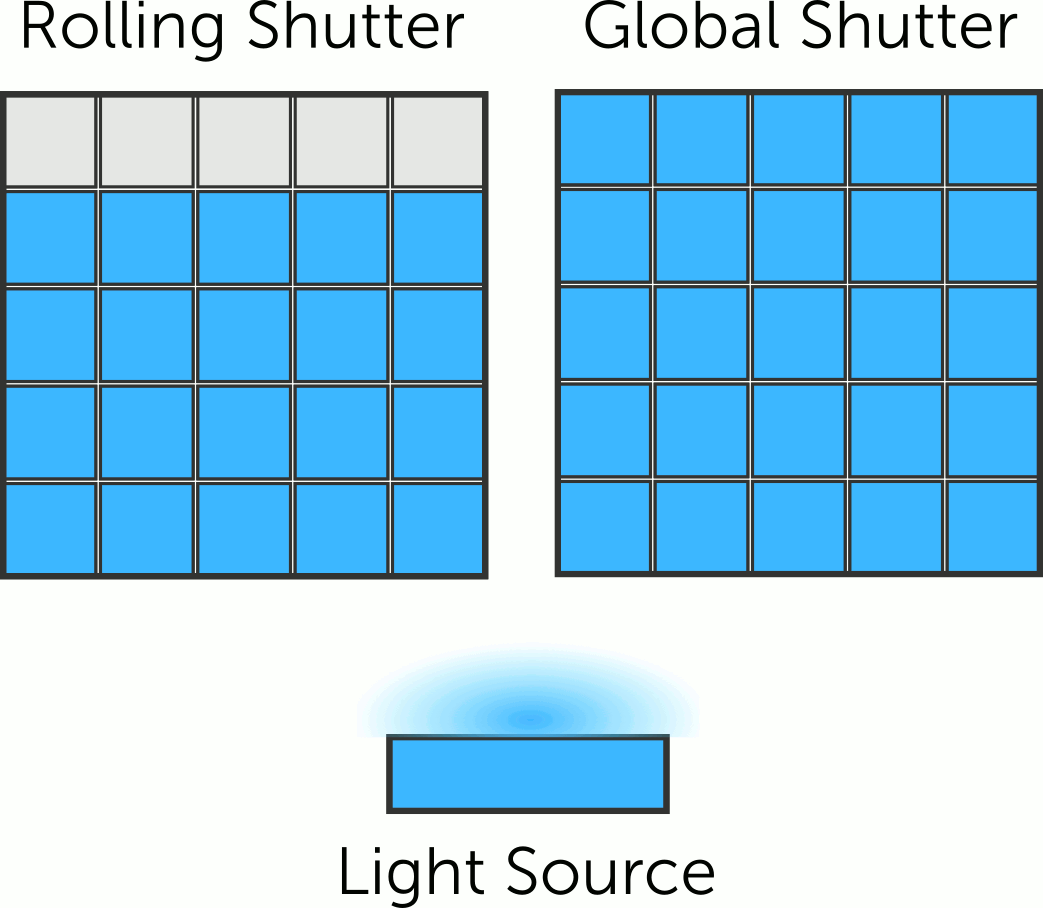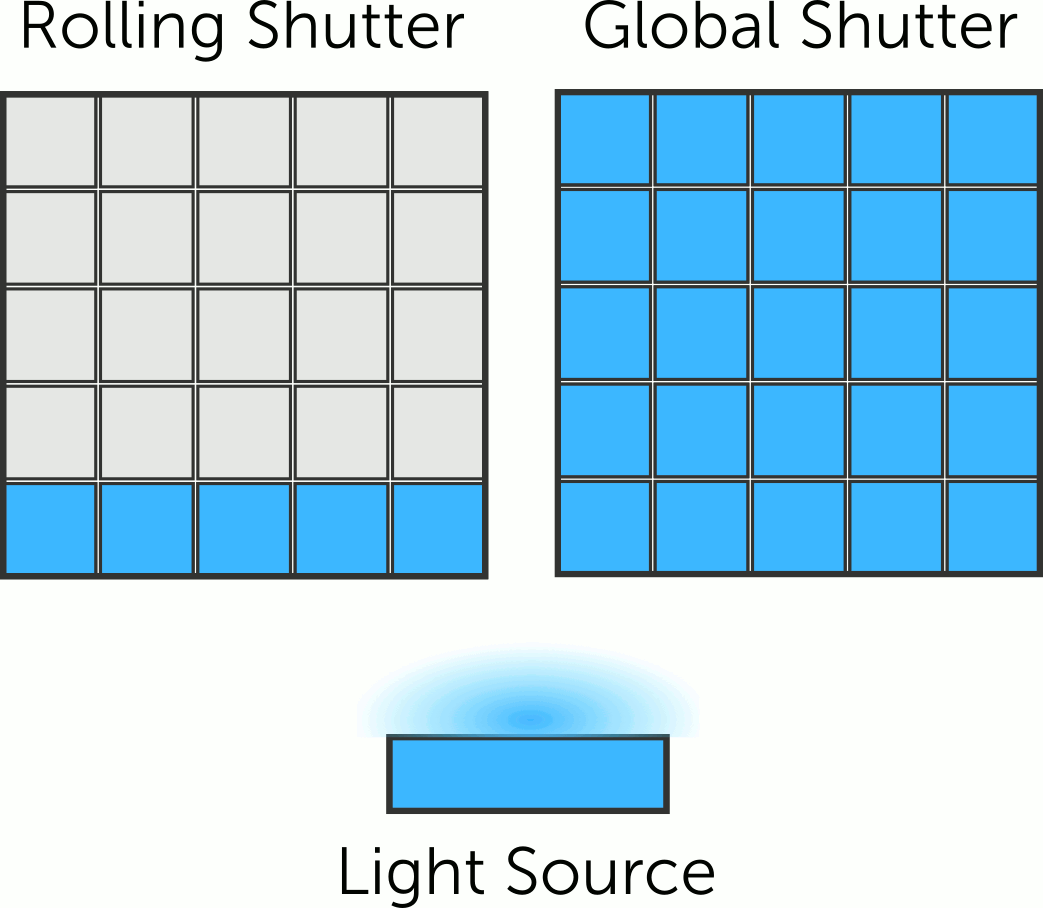
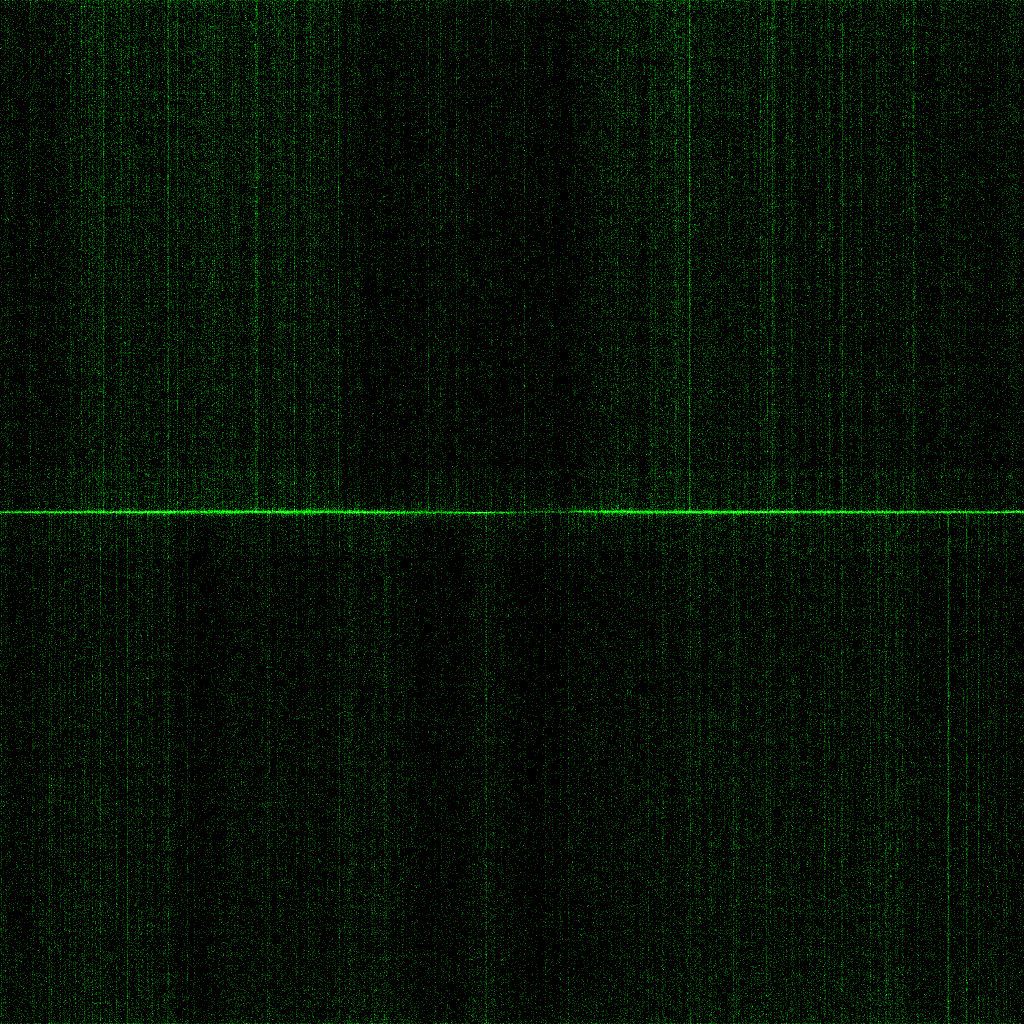
Rolling vs Global Shutter
Our CCD, EMCCD and CMOS camera ranges use electronic shutters, which differ in terms of how the sensor is read out after exposure. The two main shutter formats at play here are the global shutter and rolling shutter.
How do these shutter formats differ, and how can they affect your imaging? Find out more in this article!
Pattern Noise: DSNU and PRNU
As well as sources of random noise, such as read noise and photon shot noise, scientific cameras also encounter pattern noise, persistent noise dependent on the design and format of a camera sensor. The two factors that are largely responsible for pattern noise are DSNU and PRNU
In this article we explore DSNU and PRNU, how they can affect imaging with typical CMOS, and how we avoid these noise sources.
Triggering
Triggering allows for fine control over your imaging hardware, where components such as the light source can be used to control a scientific camera or vice versa. This is useful when exposure or acquisition needs to be synchronized with other imaging components, and this triggering can be done internally, externally, and in software or using our hardware advancing triggering cables.
Read all about the different formats of triggering, and how they can be used to advance your imaging!


Dark Current
Dark current is a time- and temperature-dependent factor that can cause the build-up of noise on the camera sensor. The longer the exposure the greater the contribution of dark current, and this factor is why cameras often come equipped with cooling options and hot pixel corrections.
In this article we outline dark current, dark current noise, hot pixels, and how new CMOS technologies allow for ultra-low dark currents and long-exposure imaging, such as the Retiga E7!
